Why do industrial robots use gearboxes?
In the field of industrial robotics, students who are new to the mechanical field may wonder: why not just use motors to control the robot's joint movements? In fact, the power source of industrial robots is usually AC servo motors, which can flexibly adjust the speed according to the pulse signal, so does it seem redundant to add a gearhead? Today, we will unveil the mystery of the reducer, analyze its important role in industrial robots.
What is a speed reducer?
As defined by Wikipedia, a gearbox is a self-contained, closed-end transmission device used primarily to reduce speed and increase torque for a variety of mechanical tasks. So, why is there a need to reduce speed and increase torque? Let's find out through gear movement.
When analyzing gears for power calculations, think of a gear as a lever. The point of contact of the gear is the end of the lever's force arm, while the center of the gear's circle is the lever's fulcrum. Through this simplification, we can arrive at the formula that at the same power, the rotational speed is inversely proportional to the torque. Therefore, gearboxes are designed precisely to reduce the rotational speed while increasing the torque to ensure that the machine can run stably under various working conditions.

Practical requirements for industrial robots
Let's look at the actual needs of industrial robots:

>> Withstanding gravitational torque: The joints of industrial robots need to withstand the torque generated by gravity in the back-end mechanism, which places high demands on the gearheads.
>> Stabilized RPM: These joints usually do not have a high RPM, and servo motors running at very low speeds can lead to unstable control, so gearboxes are needed to keep the motors running smoothly at a reasonable RPM.
>> High-precision requirements: High-precision positioning and repetitive positioning are necessary for industrial robots to accomplish their tasks, and gearboxes play an important role in this process.
In order to solve the above problems need to find an effective solution in the torque, motor speed and accuracy of three aspects, and reducer can easily solve these problems.
By using a gearhead, for example a 50:1 gearhead, the torque of a motor rated at 100 mNm can be increased to 5 Nm. If a 5 Nm motor is used directly, a larger size is needed to ensure the output power, and the increased current will lead to overheating of the motor, shortening its service life. The heat generation of the motor using the gearbox is only 1/2500 of the original, which greatly improves the safety and reliability of operation.
Improvement of control accuracy
Industrial robot joints typically rotate at only one or two revolutions per second, while a motor rated at 100mNm can easily reach 6,000 revolutions per minute. While increasing the voltage can increase the rotational speed, the bearing and rotor capacity must be considered. With the use of a speed reducer, speed control will be more precise, reducing high-frequency noise due to quantization and resulting in smoother motion. The speed reducer increases the rotor's equivalent moment of inertia to 2,500 times, enhancing the stability of the control loop.
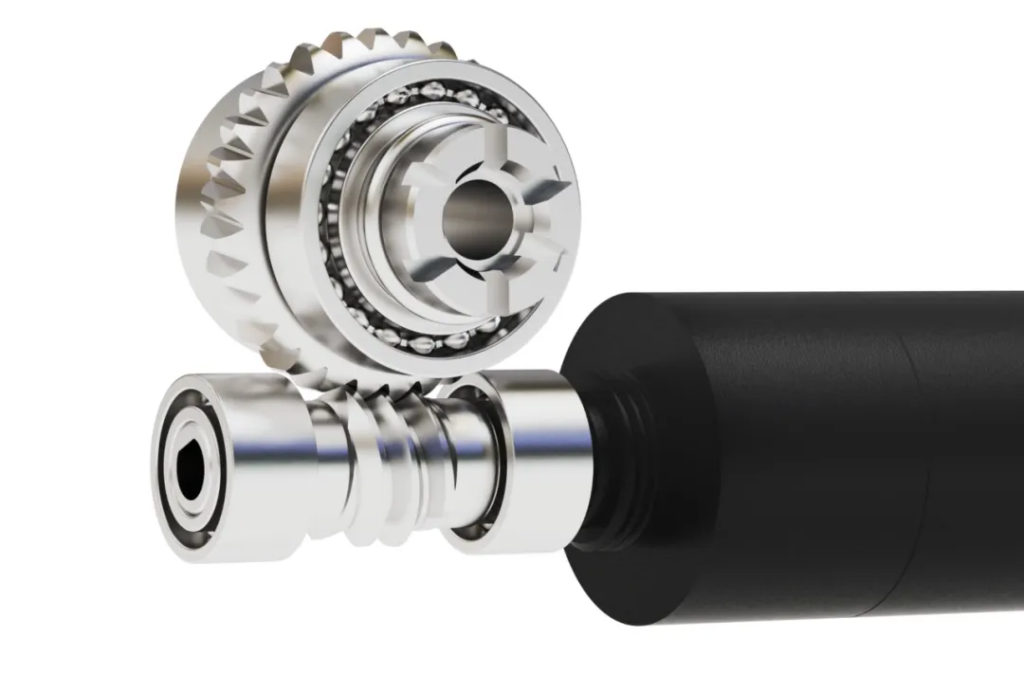

Application Cases
In articulated robots, commonly used gearheads include RV gearheads, harmonic gearheads, and ring-enveloped worm gearheads. rV gearheads have high stiffness and rotary accuracy, making them suitable for use in heavy-loading positions, while harmonic gearheads are mostly used in positions such as small arms and wrists. The natural 90° output structure of the ring-enveloped worm gear reducer and the multi-tooth mesh design also allow for great torque and precision, and are also well suited for use in all types of joints, and they are currently found in dexterous hand joints, where their cost is lower compared to RV reducers. Their respective design features enable industrial robots to demonstrate superior performance in different operating scenarios.
Reduction gearboxes play an indispensable role in industrial robots, helping them to achieve efficient and stable operation under various working conditions. The high price of gearboxes reflects the technical barriers in the market, which requires a high degree of material science, precision machining and assembly technology, making it no easy task to manufacture high-quality gearboxes.
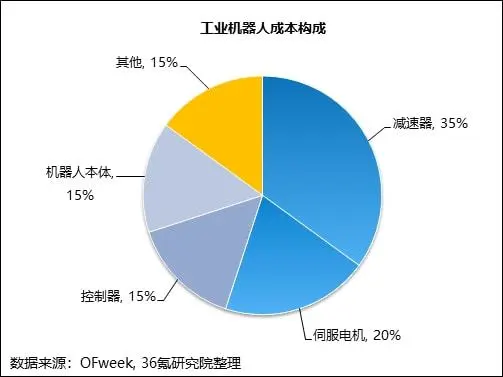
If you found this knowledge helpful, please share it with more friends and we'll see you in the next issue!
 Taoshi Intelligent Technology
Taoshi Intelligent Technology

